The principle of freeze dryier to remove water by sublimation and collect by condensation. The freeze-drying process is divided into three stages: (Product freezing stage,primary lyophilization stage; secondary lyophilization stage,<1% water remained)
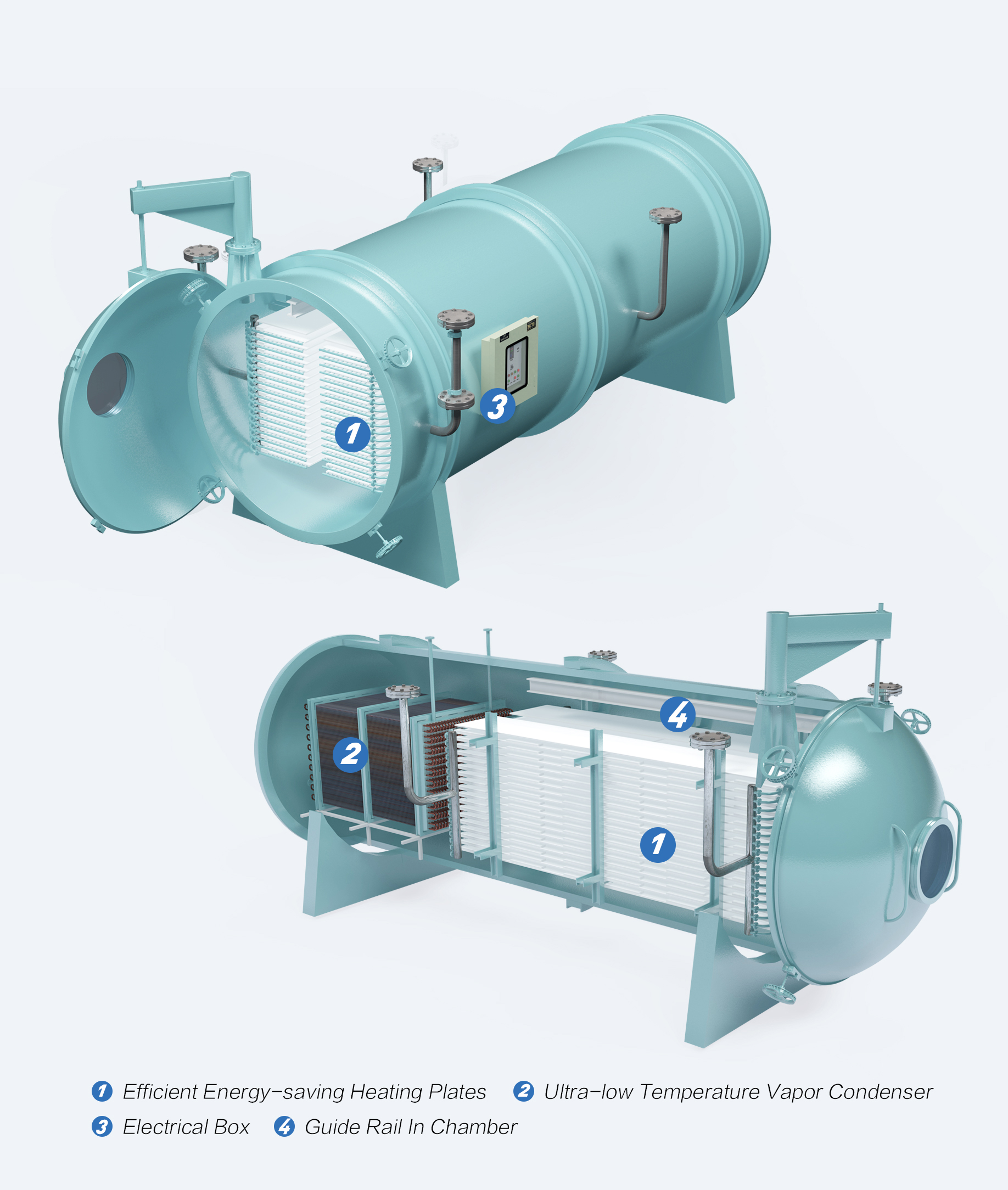
The Vacuum Freeze Dryer represents a sophisticated dehydration technology that employs a combination of multidisciplinary development methods such as refrigeration, heating, vacuum, biological, electrical, and more. This process freezes hydrous materials at low temperatures and subsequently utilizes a thermal radiation technique to heat them under vacuum conditions, thereby sublimating ice directly into gas. Once the moisture has been removed, an ice-condenser (cold trap) and vacuum device are employed to dehydrate the remaining water content.
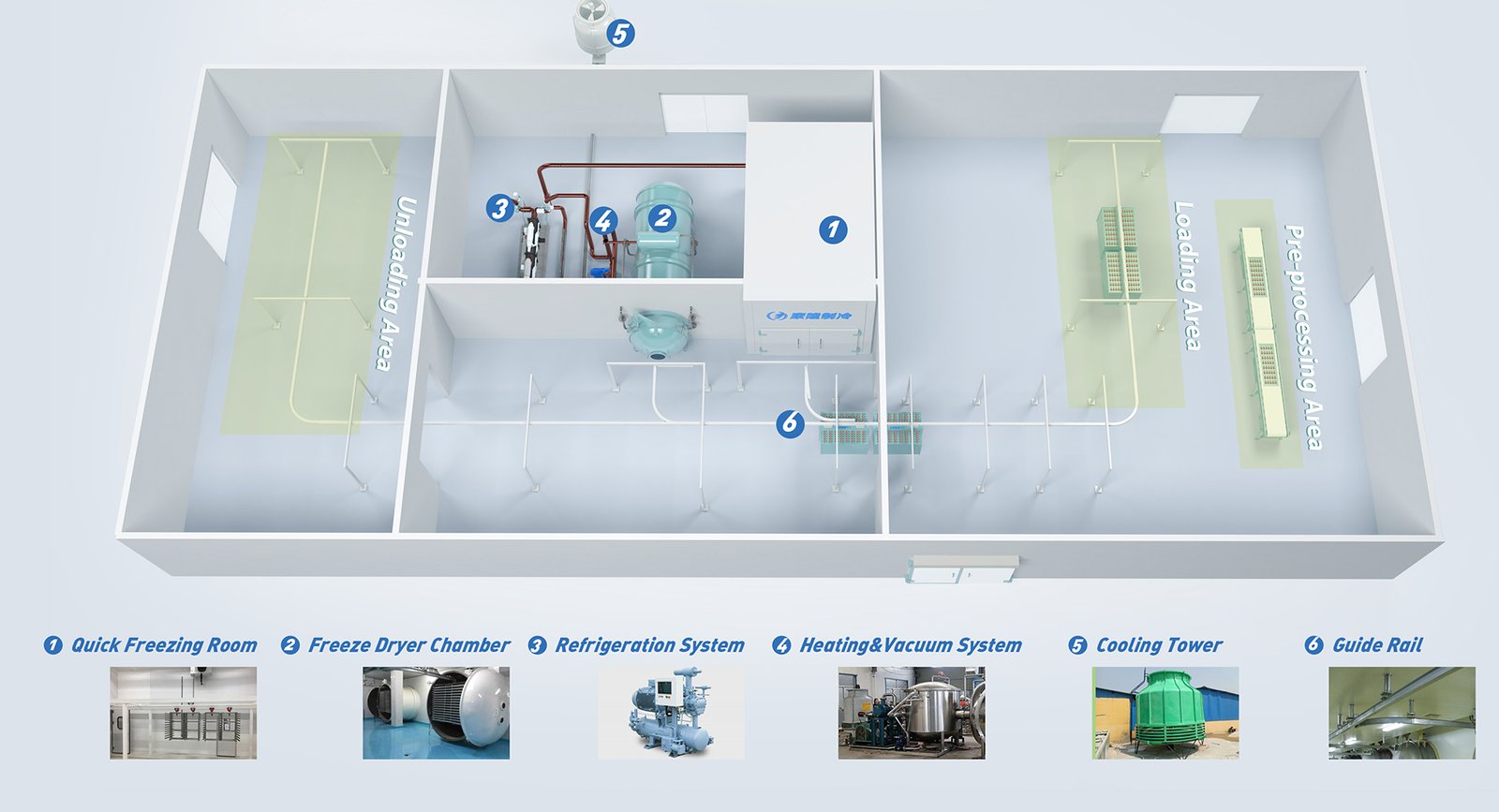
The KFD series vacuum freeze dryer comprises of several subsystems, namely the material quick freezing system, vacuum tank system, heating system, vacuum system, refrigeration system, material transfer system, electric control system, pneumatic system, and disinfection system. The overall system is optimized with a reasonable, economic and advanced design, and is highly efficient, automated, energy-saving, easy to operate, and convenient to maintain.
The vacuum system employs a combination of water ring pump or oil seal pump with multi-stage roots pump to remove air quickly and maintain vacuum conditions with small power, thus reducing energy consumption. The water ring pump eliminates water content and overcomes the disadvantages of the oil seal pump’s poor drainage performance, oil emulsification, and vacuum instability.
The heating system utilizes a sealed water circulation system with an automatic compression function and a 3-way regulated valve to adjust the heat of the water circulation system. The automatic compression system can guarantee hot water temperature up to +120°C, which increases the thermal efficiency.
The refrigeration system uses Freon refrigeration for small to medium-sized models and ammonia single-phase circulation refrigeration for large models. The expansion valve automatically adjusts the liquid flow, while the ice-condenser applies a postposition type cold trap with short pipes connection, little resistance, and smooth moisture and gas access. The water catch is efficient, energy-saving, and even.
The electric control system employs intelligent instruments and a PLC system with touch screen control and computer monitoring. It features an automatic control system with ten-time periods control for the freeze-drying curve, specialized for food lyophilization. The system allows for easy and convenient curve parameter setting, high reliability, and good accuracy. It also has the function of storing and querying historical data, facilitating production process analysis.
Vacuum freeze drying is a state-of-the-art dehydration technology that involves freezing hydrous material at low temperatures, and then using thermal radiation to heat it under vacuum conditions, thereby sublimating ice directly into gas. After removing the moisture, it employs an ice-condenser (cold trap) and vacuum device to dehydrate the remaining water content. This is a combined application technology based on multidisciplinary development, including refrigeration, heating, vacuum, biological, electrical, and more.
Vacuum freeze drying technology has a wide range of applications, including chemical products, biologics, health products, herbs, and agricultural products such as meat, poultry, eggs, seafood, vegetables, fruits, and more.
The vacuum freeze drying process can be broken down into three main stages.
1. The first stage is the quick freezing of the material. During this stage, the water content in the products turns into a solid state from a liquid state by freezing. The final frozen temperature should be below the eutectic point temperature, which is determined by testing the material to ensure that it is fully frozen. The freezing speed of the material depends on its characteristics, and a quick blast freezing room is used for pre-freezing.
2. The second stage is the primary dehydration stage, also known as the sublimation dehydration stage. The frozen material with a temperature below the eutectic point is dehydrated in a vacuum condition by sublimation to remove its moisture.
During sublimation, the heating plate temperature and vacuum condition must be strictly controlled to prevent the material from melting or the temperature from rising above the eutectic point.
The temperature of the dried parts must also be prevented from rising above their disintegration temperature, which can cause a change in shape or even collapse. During this stage, the heating plates heat the material by thermal radiation or provide the energy for sublimation. The vacuum tank must be under vacuum condition, and the ice-condenser (cold trap) catches the moisture that comes from the material and condenses it to ice on the surface of the cold trap coils.
3. The third stage is the secondary dehydration stage, also known as desorption drying. The purpose of this stage is to remove bound moisture. Because the adsorption energy of bound moisture is very high, a large amount of heat energy must be provided in this stage. This means that the heating plate temperature will be slightly higher to approach the highest temperature that the material can bear. When the material moisture is within the specified range, the final dehydration is complete.
4. To determine whether the vacuum freeze drying process is complete, it can be based on experience of the material temperature curve, sample status, shape, and other factors. The process can also be evaluated using terminal point testing, such as air pressure increases.
| KFD-5 | KFD-10 | KFD-25 | KFD-50 | KFD-100 | KFD-150 | KFD-200 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drying Area(m²) | 5 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 100 | 150 | 200 |
| Equipment Floor Area (m2) | 12 | 24 | 50 | 86 | 130 | 190 | 260 |
| Advise Minimum Usable Area (m2) | 22 | 45 | 80 | 180 | 255 | 330 | 450 |
| Size Of Material Tray(mm) | 780×540×30 | 540×645×30 | 540×645×30 | 540×645×30 | 540×645×30 | 540×645×30 | 540×645×30 |
| Number Of Material Tray(pcs) | 12 | 24 | 72 | 144 | 288 | 438 | 576 |
| Size Of Tank(m) | Ф1.0×3.4 | Ф1.5×3.2 | Ф1.88×4.2 | Ф2.0×8.16 | Ф2.4×10.2 | Ф2.4×13.9 | Ф2.4×17.8 |
| Operation Vacuum(Pa) | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa | 13.3-133 Pa |
| Heating Plate Temp.(℃) | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ | Normal temperature~+120℃ |
| Electric Heating(Kw) | 12 | 21 | 50 | / | / | / | / |
| Steam Consumption(kg/h0.7mPa) | / | / | / | 150 | 300 | 450 | 560 |
| Consommation de charge à froid (kw) | 12 | 22 | 45 | 90 | 180 | 270 | 360 |
| Installation Power(Kw) | 22 | 53 | 112 | 213 | 289 | 370 |
2. Different defrosting methods are available, including one-time water defrosting, steam defrosting, and automatic alternated defrosting.
3. The size of the freeze dryer varies according to capacity, including mini lab, medium production, and large-scale production types. Custom sizes are also available.
4. The KFD series freeze dryer uses two heating methods: electric heating for mini and medium-size models, and steam heating for large-scale models.
5. The refrigeration system of the FD series freeze dryer uses either Freon or Ammonia. The table specifies the parameters for Freon refrigeration systems.
6. It is recommended to have a minimum usable area that includes equipment floor area, equipment maintenance space, and processing materials flow area. Multiple sets of equipment can save space and be designed according to specific needs.